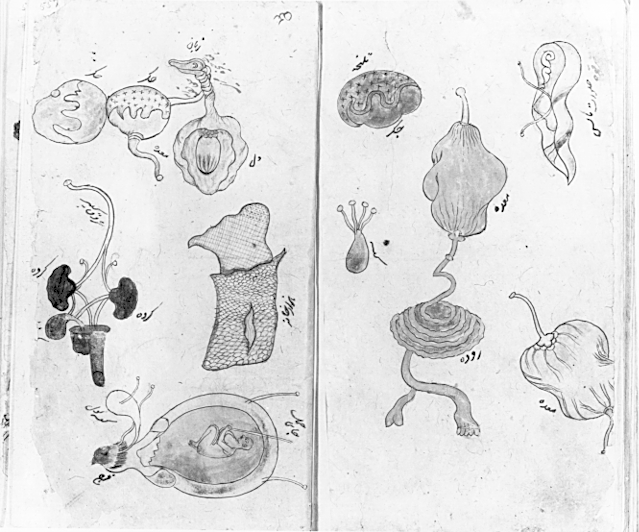Islamic Empire Achievements In Medicine
The islamic world was far ahead of the western world in the middle ages.

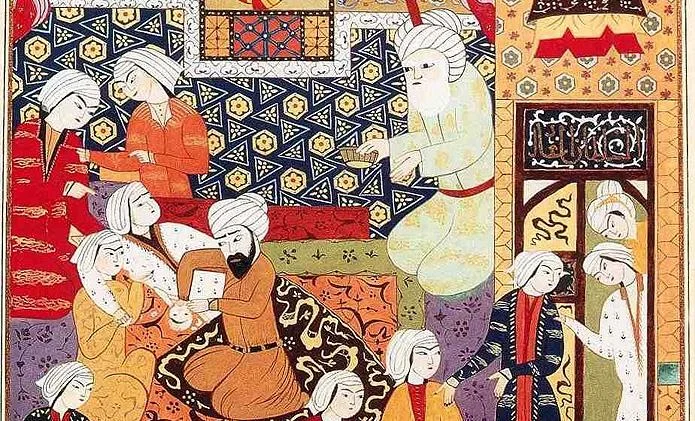
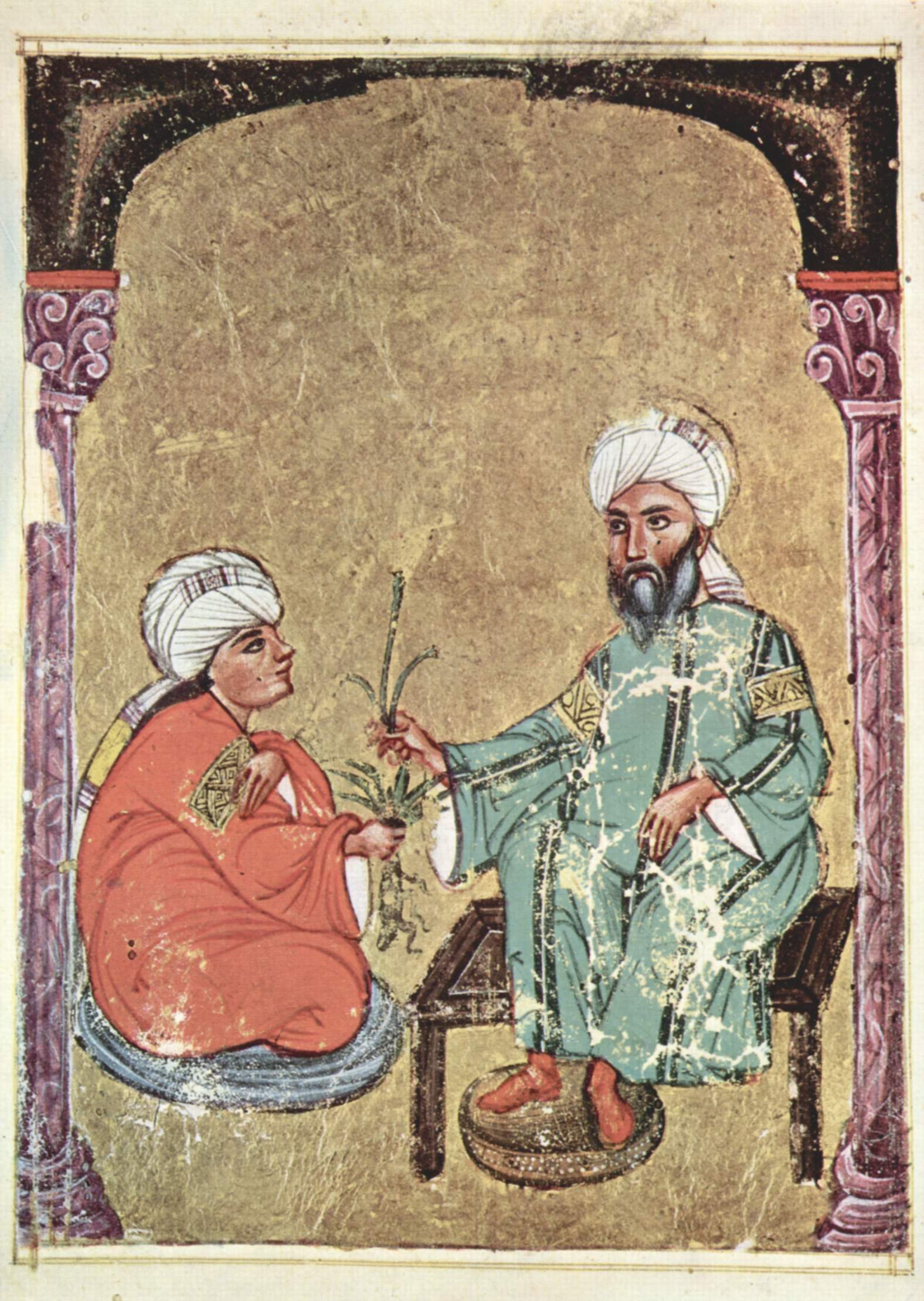
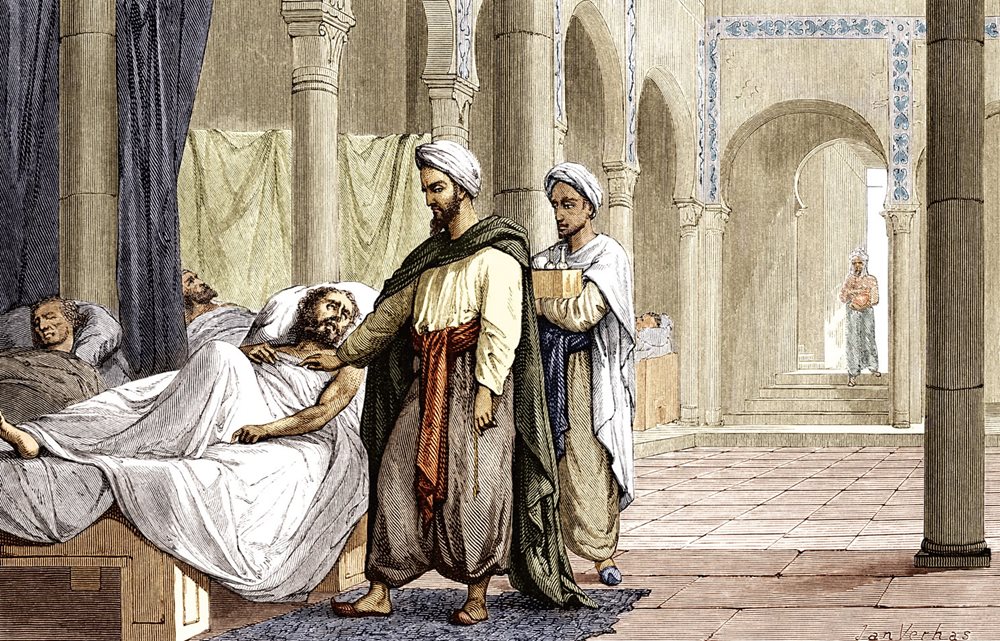
Islamic empire achievements in medicine. The islamic golden age contributed to the invention of the modern teaching hospital and a medical encyclopedia that served europe for the next 600 years. Pursuing the philosophy that for every disease allah has given a cure islamic scientists made significant achievements in medical practice and education as well as pharmacology. For islamic scholars indian and greek physicians and medical researchers sushruta galen mankah atreya hippocrates charaka and agnivesa were pre eminent authorities. The major contribution of the islamic age to the history of medicine was the establishment of hospitals paid for by the charitable donations known as zakat tax.
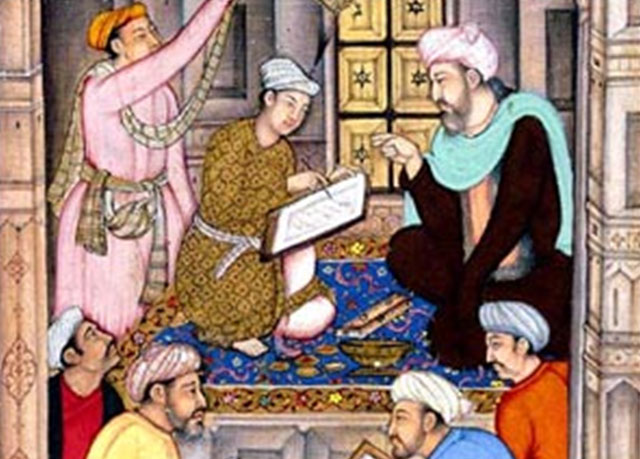
In order to make the indian and greek tradition more accessible understandable and teachable islamic scholars ordered and made more systematic the vast indian and greco roman medical knowledge by writing encyclopedias and summaries. The abbasid empire also saw the origins of the scientific method along with the development of chemistry physics and astronomy as discrete fields of inquiry. He wrote a great medical treatise the kitab al tasrif a 30 volume book of medicine and surgery. Muslim scholars knew of many books written not only by.
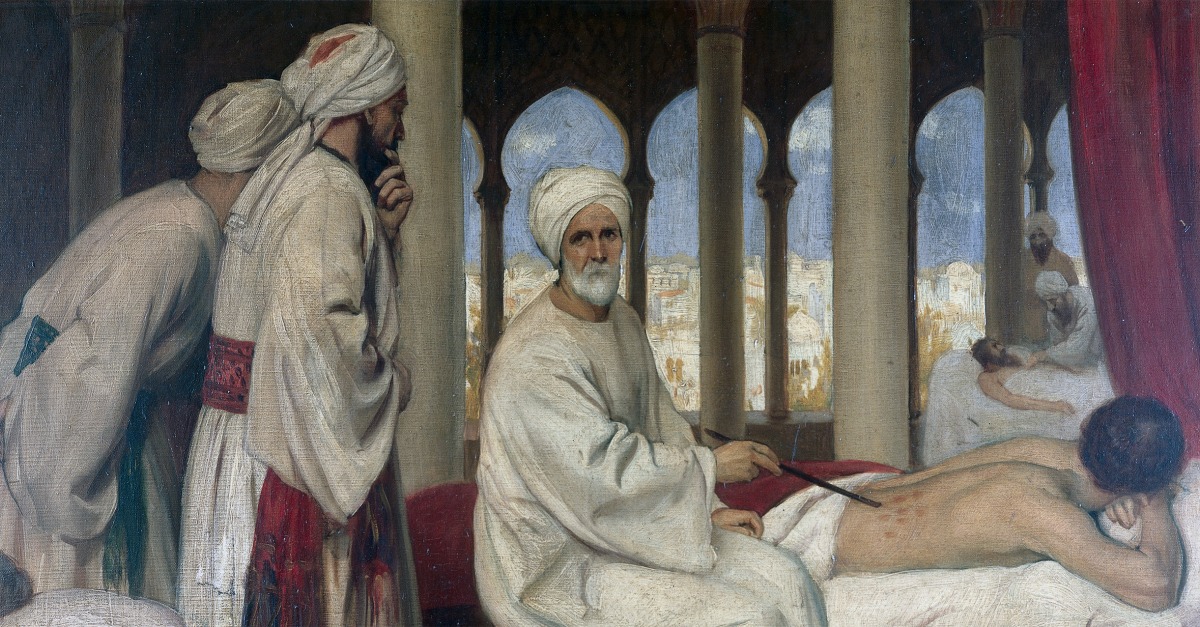
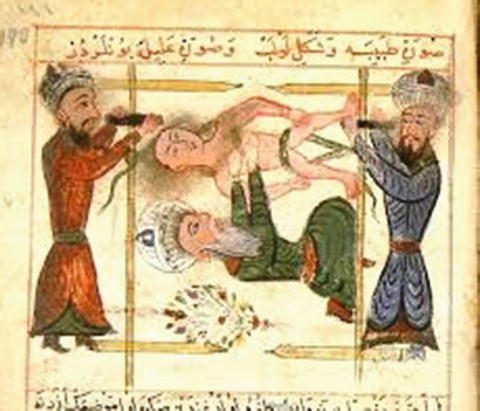
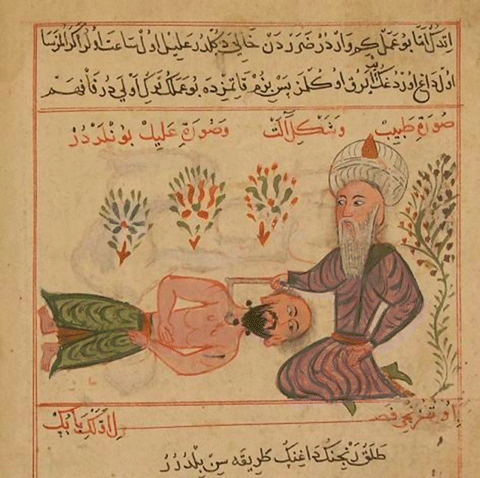
Early muslim medicine drew on traditional practices from the region some dating back to ancient mesopotamia and ancient babylon in the third millennium bc. Islamic achievements in medieval medicine. The 10th century arabic doctor al zahrawi established the basis of surgery in al andalus in cordoba where he worked as a doctor for the caliph al hakam ii. Surgery and surgical instruments.
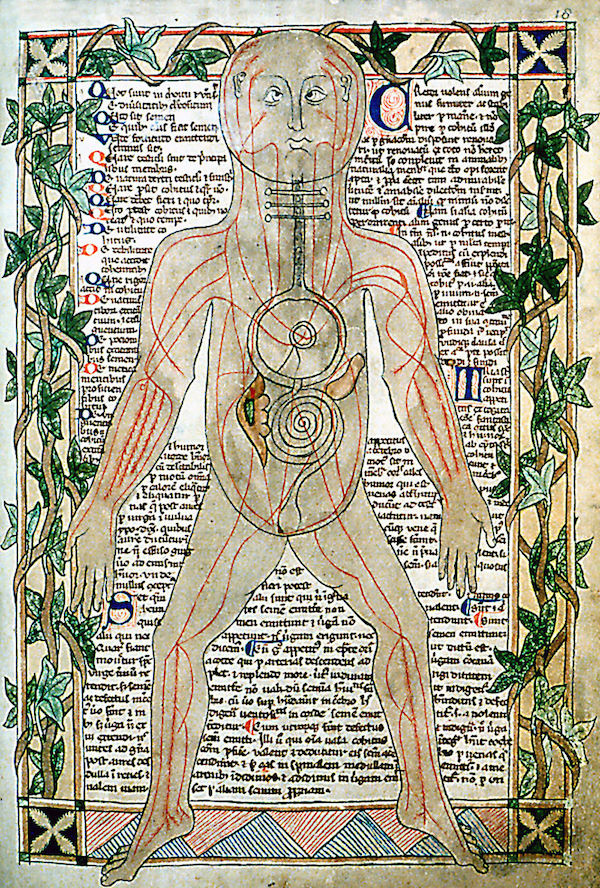
Science medicine and everyday life in the islamic world. Medieval islams receptiveness to new ideas and heritages helped it make major advances in medicine during this time adding to earlier medical ideas and techniques expanding the development of the health sciences and corresponding institutions and advancing medical knowledge in areas such as surgery and understanding of the human body although many western scholars have not fully acknowledged its influence independent of roman and greek influence on the development of medicine.